WebSockets are a type of protocol that enables two-way communication between a client (such as a web browser) and a server over a single, long-lived connection. Unlike traditional HTTP requests, which are stateless and require the client to initiate a new request each time it needs to communicate with the server, WebSockets allow for real-time, bi-directional communication between the client and server, with minimal latency and overhead.
WebSockets use a standardized protocol, which allows the client and server to exchange data in a structured format. This protocol includes a handshake mechanism that establishes the connection between the client and server, as well as mechanisms for sending and receiving messages in both directions.
WebSockets are commonly used in applications that require real-time data updates or push notifications, such as chat applications, real-time gaming, and stock trading platforms. They can also be used to enhance the performance of web applications by reducing the number of HTTP requests required to update content or retrieve data from the server.
In simple words
WebSockets are like having a secret phone line between your computer and a website. Normally, when you visit a website, your computer sends a message to the website's computer and waits for a response before sending another message. But with WebSockets, your computer can talk to the website's computer whenever it wants, and the website's computer can talk back, all without having to wait for each other. This is really useful for things like playing games online or chatting with friends in real-time, because you can send messages back and forth quickly without any delays.
Architecture
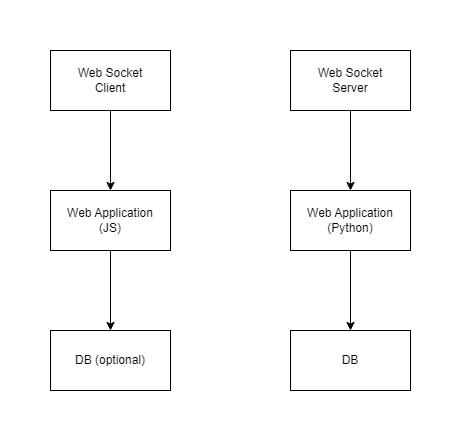
In this architecture diagram, the WebSocket client is implemented in JavaScript and runs in a web browser. The WebSocket server is implemented in Python using the websockets library, and runs on a web server. The web server also serves static files for the web application.
Optionally, the chat application may also use a database to store chat messages or user information. The database can be implemented using any appropriate database technology, such as MySQL or PostgreSQL.
When a user opens the chat application in their web browser, the web application sends a request to the web server to establish a WebSocket connection. The web server handles the WebSocket connection using the websockets library, and forwards messages between the WebSocket client and the WebSocket server.
The WebSocket client sends chat messages to the WebSocket server, which handles the incoming messages and forwards them to all connected clients. The WebSocket server also receives chat messages from other clients and forwards them to the WebSocket client, which displays them in the chat application.
If a database is used, the WebSocket server may store chat messages or user information in the database, or retrieve data from the database as needed.
Now look at the sample code
# server.py
import asyncio
import websockets
async def handler(websocket, path):
async for message in websocket:
print(f"Received message: {message}")
await websocket.send(f"Server received your message: {message}")
async def main():
async with websockets.serve(handler, "localhost", 8765):
await asyncio.Future()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
# client.py
import asyncio
import websockets
async def send_messages():
async with websockets.connect("ws://localhost:8765") as websocket:
while True:
message = input("Type a message to send to the server: ")
await websocket.send(message)
response = await websocket.recv()
print(f"Received response: {response}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(send_messages())
In this example, the server listens on localhost:8765 for incoming WebSocket connections. The handler function is called for each incoming connection, and waits for messages from the client using an asynchronous for loop. When a message is received, it prints the message to the console and sends a response back to the client using the websocket.send method.
The client connects to the server at ws://localhost:8765 using the websockets.connect method. It then enters a loop that prompts the user to enter a message, sends the message to the server using the websocket.send method, waits for a response using the websocket.recv method, and prints the response to the console.
To run this example, you can save the server and client code to separate files (e.g. server.py and client.py), and then run the server in one terminal window and the client in another terminal window. You should see the messages you send from the client appear in the server console, and the server responses appear in the client console.
Take-away
In conclusion, building a WebSocket-based chat application using Python and websockets can provide a powerful real-time communication platform for web applications. With websockets, data can be transmitted between a client and server without the need for polling or long-polling techniques. Python's websockets library provides an easy-to-use solution for implementing WebSocket servers, and with the addition of a web application and web server, a complete chat application can be developed. Optional integration with a database can provide persistent storage for chat messages or user information. Overall, WebSocket-based chat applications offer a modern and efficient approach to real-time communication in web applications.